New pollutant standard material-source brief description
What are the new pollutants?
New pollutants refer to those toxic and harmful chemicals that have the characteristics of biotoxicity, environmental persistence and bioaccumulation.
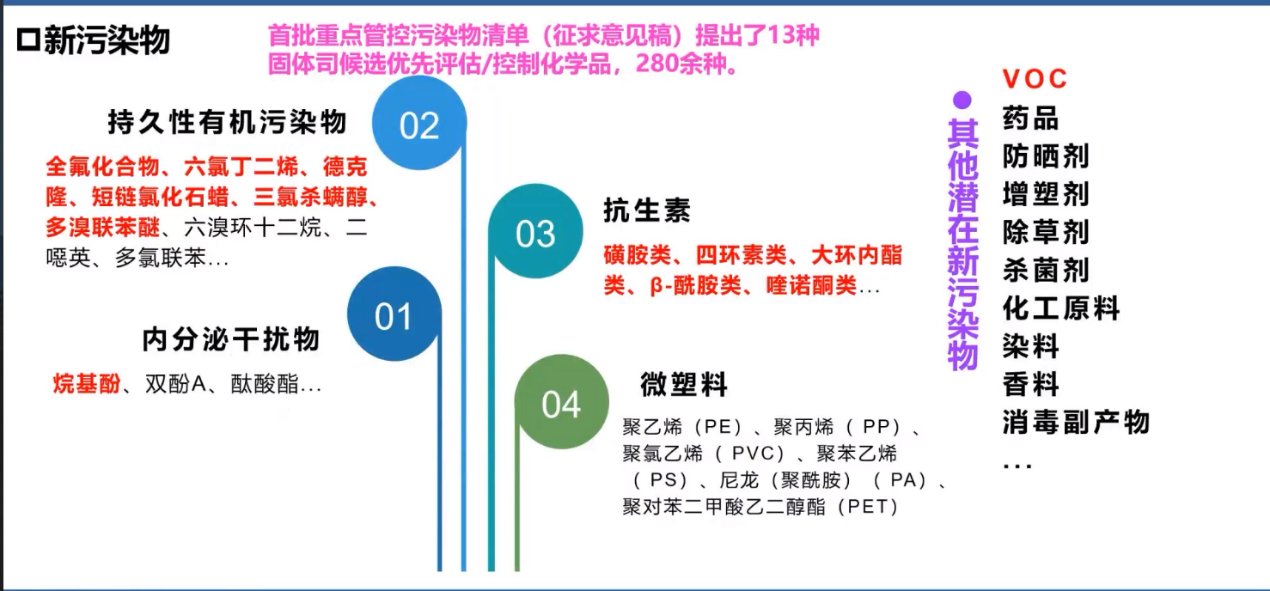
There are four major categories of new pollutants of wide concern:
1, persistent organic pollutants 2, endocrine disruptors 3, antibiotics 4, microplastics.
characteristic:
(1) High biotoxicity: new pollutants often have the characteristics of carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, mutagicity and endocrine system interference affecting reproduction and development, such substances are more harmful to organisms;
(2) Persistence: not easy to degrade in the environment, long retention time;
(3) Accumulation: easy to enrich, long-distance migration or transmission along the food chain, the higher the cumulative concentration in the more advanced the organism;
(4) Concealed: For substances that have been produced and used for many years, their harm is often ignored and difficult to detect. At the same time, there is also a short-term harm is not obvious, but the long-term even in the low concentration may also have greater risks to the human body and the environment characteristics;
(5) Not easy to control: there are a wide variety of new pollutants, wide sources, difficult monitoring, the harm, transformation and migration mechanism is unknown, and it is difficult to control.
Common persistent organic pollutants include perfluorosynsulfonic acid and its salts and fluoride (PFOS), perffluoroic acid (PFOA) and its salts and related compounds, chlorbromodiphenyl ether, short chain chlorofaffin, hexaclobutadiene, pentacphenol and its salts and esters, trichloroidol, perfluorohexadiosulfonic acid and its salts and related compounds PFHxS, cloning, etc.
Ruiling Technology can provide a full set of new pollutant standard materials, which can be traced back to the international authorities (NIST and NPL), and the standard materials are:
1.Perfluorsulfonic acid and its salts and fluoride (PFOS)
2.Perfluoroic acid and its salts and related compounds (PFOA)
3.decabromodiphenyl oxide;
4.Short-chain chloroparaffin;
5.hexachlorobutadiene;
6.Pentachlorohydrophenol and its salts and esters;
7.dicofol;
8.Perperfluorohexyl sulfonic acid and its salts and related compounds (class PFHxS);
9.The clone and its cis isomer and trans isomer;
10. dichloromethane;
11, Tricloromethane;
12, Nonylphenol;
13, Antibiotics (sulfonamides, tetracyclines, macrolides, β -amides, quinolones)
14, Hexamediane, chlorotan, ant spirit, hexachlorobenzene, DDT, α -hexane, β -hex, lintan, sultanogen and its related isoforms, PCBs